Materials Breakdown for DIY 6x8 Shed Construction
Constructing a DIY shed offers a rewarding experience, providing valuable storage space and enhancing property aesthetics. However, a successful project necessitates careful planning and the acquisition of appropriate materials. This comprehensive guide details the materials required for building a 6x8 shed, emphasizing quality and longevity. The quantities provided are estimates and may need adjustment based on specific design choices and local availability.
Foundation Materials
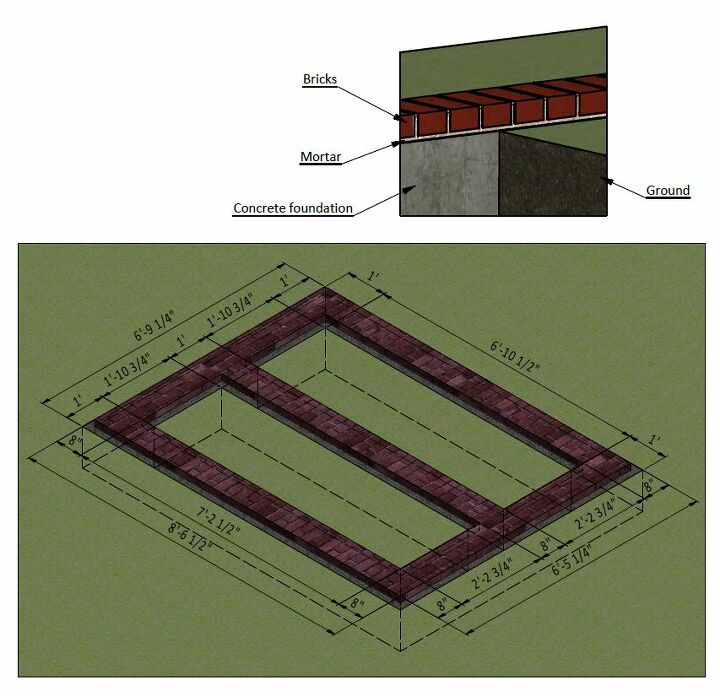
A robust foundation is paramount for a durable shed. The choice of foundation depends on several factors, including soil conditions, local building codes, and personal preference. This section outlines materials for a concrete slab foundation, a popular and reliable option.
Concrete
Quantity: Approximately 3-4 cubic yards. This estimate accounts for a 4-inch thick slab. Adjust this based on soil conditions and local building codes. Consult a concrete supplier for precise calculations given your specific site requirements.
Type: Use a standard ready-mix concrete designed for outdoor applications and capable of withstanding freeze-thaw cycles. Consider adding a concrete admixture to enhance strength and durability, especially in regions with harsh winters.
Formwork Materials
Creating the formwork requires lumber to contain the wet concrete.
Lumber: Pressure-treated 2x4 lumber is recommended for its resistance to rot and insect damage. The quantity depends on the perimeter of the shed and the height of the forms (typically 4 inches). Plan for approximately 50-75 linear feet.
Plywood or OSB: Sheets of plywood or oriented strand board (OSB) create a smooth, level surface for the concrete. Consider using ½-inch thick material. The number of sheets required will depend on the area of the shed's footprint. Calculate the area and determine the number of sheets necessary, adding extra for potential waste.
Reinforcement
Reinforcing the concrete slab increases its strength and prevents cracking.
Rebar: #4 or #5 rebar (reinforcing bars) should be spaced approximately 12 inches apart in both directions. Calculate the linear feet needed based on the dimensions of the slab. Add extra for overlaps and cutting losses.
Other Foundation Materials
Framing Materials
The shed's frame provides structural integrity and supports the walls and roof. Pressure-treated lumber is highly recommended for its resistance to decay and insect infestation, especially for the sill plate and foundation contact points. Untreated lumber can be used for other framing elements but should receive appropriate treatment for added protection.
Sill Plate
Lumber: Pressure-treated 4x6 lumber, the length matching the shed's perimeter.
Floor Joists
Lumber: Pressure-treated 2x6 or 2x8 lumber, spaced 16 inches on center. The length depends on the shed's width. Remember to calculate the number of joists required based on the 16-inch spacing.
Wall Studs
Lumber: 2x4 lumber, spaced 16 inches on center. The height of the studs should match the wall height of the shed, plus an additional length for the top and bottom plates. Calculate the quantity needed based on the wall lengths and 16-inch spacing.
Top and Bottom Plates
Lumber: 2x4 lumber, running horizontally at the top and bottom of the walls. The length of each plate must match the wall lengths.
Rafters
Lumber: 2x4 or 2x6 lumber, depending on roof pitch and local snow load requirements. Calculate the number and length of rafters based on the shed’s dimensions and desired roof pitch.
Ridge Board
Lumber: A 2x4 or 2x6 lumber piece running along the peak of the roof. The length depends on the shed's length.
Sheathing and Roofing Materials
These materials provide weather protection and structural support.
Sheathing
Plywood or OSB: ½-inch thick plywood or OSB sheets are commonly used for wall sheathing. Calculate the required number of sheets based on the wall areas, accounting for overlaps and waste.
Roofing
The choice of roofing material significantly impacts the shed's lifespan and aesthetics. Several options exist, each with varying costs and maintenance requirements.
Underlayment
Felt Paper or Synthetic Underlayment: A waterproof barrier placed beneath the roofing material to prevent leaks. Purchase sufficient material to cover the entire roof area, allowing for overlaps.
Door and Window Materials
These materials are crucial for functionality and ventilation.
Fasteners and Other Hardware
A wide variety of fasteners and hardware are essential for assembling the shed.
Siding Materials
The choice of siding depends on aesthetic preference and budget. Options include:
This comprehensive materials list provides a solid foundation for your 6x8 shed project. Remember to adjust quantities based on your specific design and local conditions. Always consult local building codes and obtain necessary permits before commencing construction. Careful planning and the procurement of high-quality materials will ensure the longevity and functionality of your new shed.
0 comments:
Post a Comment